FPDメーカーのQ3’22業績 (Samsung編)
冒頭部和訳
半導体のパンデミックブームが終わり、コンシューマー・エレクトロニクス需要は弱体化しているが、Samsung Electronicsは引き続き複数の事業から強力な収益と利益を生み出し、ディスプレイ事業による利益はLCD生産終了後のQ1に新記録を樹立した。LCDに依存する競合FPDメーカーが今四半期に深刻な損失を被った一方で (関連記事) 、SamsungはOLED販売で利益を生み出している。
Samsung’s Profits Decline But Display Sets Profit Record
Although the pandemic boom in semiconductors is over, and consumer electronics demand has weakened, Samsung Electronics continued to generate strong revenues and profits from multiple businesses, and its display business set a new profit record in the first quarter after ending LCD production. While competing display makers reliant on LCD suffered severe losses in the quarter (see separate story), Samsung generated profits selling OLED panels.
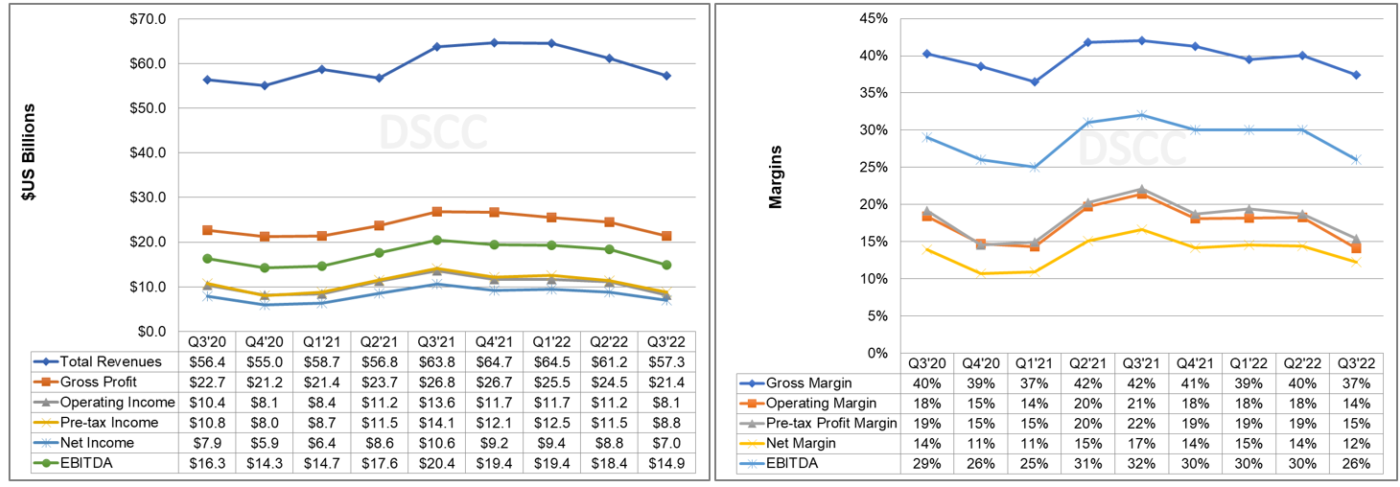
Samsung earned net income of KRW 9.4T ($7.0B) on revenues of KRW 76.8T ($57.3B). Revenues fell 2% short of consensus and net income was 1% lower than consensus. Revenues in $US decreased by 10% Y/Y and net income in $US decreased by 34% Y/Y. Currency effects resulted in a positive KRW 1T gain in operating profit; the KRW depreciated 6% Q/Q and 13% Y/Y. Samsung operating profit was KRW 10.9T ($8.1B), 12% lower than analyst expectations and down 28% Y/Y in $US.
Samsung Electronics Income Statement and Margins
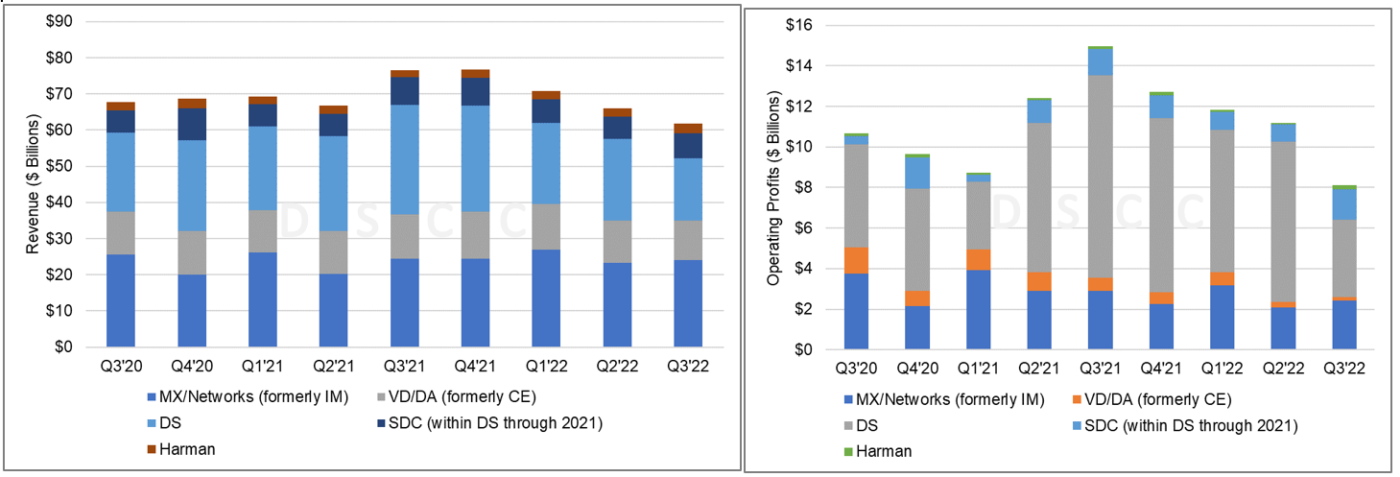
Samsung’s biggest profit driver, its DS or Device Solutions business segment (formerly called Semiconductors), stumbled as shipments and prices both declined sequentially. Device Solutions revenues decreased 34% Y/Y in KRW and decreased 43% Y/Y in $US. Operating profits decreased 56% Y/Y in KRW to 5.1T ($3.8B). For DRAM, in the third quarter, bit growth declined by a percentage in the high teens and ASP fell by around 20%. For NAND in the third quarter, bit growth decreased by a percentage in the high-single digits, while ASP saw a decrease in the low 20% range. In Q3, Samsung’s Foundry business achieved its highest ever quarterly revenue and operating profit due to steady yield improvement and increased revenue contributions.
Samsung Electronics Division Revenue and Operating Profit
For MX (Mobile eXperience) business, revenue in KRW increased 10% Q/Q with new product launches. Profit in KRW increased 24% Q/Q with strong sales of premium products. Samsung’s Galaxy Fold 4 and Flip 4 launched in Q3 made great strides compared to their predecessors despite the challenging environment. Samsung believes the mainstreaming of foldables is on track. The S22 series also maintained solid sales momentum and saw significant Y-o-Y revenue growth. In mobile in the third quarter, shipments were approximately 64 million units for smartphones and 7 million units for tablets. Smartphone ASP was $282.
In Samsung’s Visual Display (VD) business, Samsung said that TV market demand increased quarter-on-quarter based on seasonality but it contracted year-on-year caused by the decrease in consumer confidence resulting from high interest rate, inflation and other macroeconomic factors. TV revenue increased 1% Y/Y in KRW but declined 13% Y/Y in $US. The operating profit of VD+DA (Digital Appliances) plummeted Y/Y by 67% due to a decrease in revenue and cost increases. For TVs, sales volume in the third quarter increased by a percentage just into the double digits sequentially.
Samsung’s Display Products division recorded an operating profit of KRW 2.0T ($1.5B), its highest profits ever, on revenues of KRW 9.4T ($7.0B). Revenues were up 15% Q/Q but down 8% Y/Y in US$ terms, while operating profit increased 76% Q/Q and 15% Y/Y. The Mobile Display business improved its result quarter-on-quarter, thanks to growth in demand attributable to launches of new models by major smartphone brands. SDC benefited in Q3 from strong sales of LTPO panels for the iPhone 14 Pro Max which carry a healthy premium. LG Display was unable to make the LTPO panels for the Pro Max, shifting revenue and profits to Samsung.
For the large display business, sales of QD-OLED products continue to rise, driven by expanding launches of QD-OLED monitors by global IT brands and ongoing improvements in our yields. However, the business deficit remained similar quarter-on-quarter due to initial investment costs. For display in the third quarter, the mobile portion of revenue was a percentage in the high 90s and sales volume declined by a percentage in the mid-single digits.
For its large panel business, Samsung reported that QD-OLED has received very positive responses from customers. SDC launched QD-OLED based monitor panels in the second half. QD-OLED yield is rapidly climbing and SDC has been diversifying its customer base and product lineup. SDC is looking into additional investment plans for QD-OLED while closely collaborating with its customers and also carefully watching market demand, so that SDC is able to supply demand without disruptions.
Samsung’s spent KRW 12.3T ($9.2B) on capital expenditures for the quarter, of which KRW 11.5T was in the DS division and KRW 0.5T in Display. Samsung expects full-year capex to reach ~KRW 54T, with KRW 47.7T for DS and KRW 3T for display. Display capex of KRW 3T will expand the capacity of flexible displays for mobile products and enhance the efficiency of large QD-OLED panel production.
For the fourth quarter of 2022, Samsung expects that macro uncertainties are unlikely to dissipate. The MX business in Q4 will continue to focus on sales of premium smartphones and expand the sales of tablets and wearables. MX expects sales volume to grow after releasing new mass model smartphones. For the fourth quarter, we expect shipments of smartphones and tablets to rise, but smartphone ASP is likely to decline.
Samsung expects DRAM market bit growth to be in the high-single digit range and Samsung bit growth should be above market. On a full-year basis, market bit growth and Samsung bit growth should be similar in the low to mid-single digit % range. In the fourth quarter, Samsung expects NAND market bit growth of a mid-single digit and Samsung should be above market. For the year, Samsung expects market bit growth to be in the mid-single digit range and Samsung bit growth should be similar.
Although Samsung expects TV market demand in Q4 to increase quarter-on-quarter due to year-end peak seasonality and global sporting events, several macroeconomic risks are likely to continue to cast uncertainties on our TV demand. For the fourth quarter, Samsung expects TV sales volume growth to be in the high 20% range. On a full year basis, sales volume will likely decline by a percentage in the low-single digits.
In Q4, SDC’s mobile panel business is expected to continue to grow on the back of strong smartphone demand for premium OLED panels. The large panel business will expand the presence of QD-OLED by capitalizing on year-end seasonality and growing our customer base. In Q4, Samsung expects smartphone market growth to be weaker than normal due to the sluggish consumer spending amid high interest rate and high prices despite continued strong seasonal effects for the smartphone and IT products.
In 2023, Samsung expects the smartphone market to grow Y/Y, led by growth in flagships. Wearables are expected to continue to see high growth in the double digits. In 2023 the tablets market for mid to low priced products is expected to contract slightly, but the market for premium tablets should stay solid. 2023 overall TV demand is projected to remain stagnant, but demand for premium products, including super big TVs, should keep growing. Samsung’s TV strategy is focused on the premium segment, especially Neo QLED (Samsung’s VD representative did not mention QD OLED TVs).
Also, in 2023 Samsung will start to boot up sales of MicroLED and will implement this into various sizes.
For 2023, SDC will strive to increase OLED market share by promoting the advantages of OLED in the new application areas, such as IT, automotive and gaming, In the AR/VR market, which is projected to enjoy full flagship growth from 2023, Samsung will develop technologies and complete upstream and downstream SCM in order to fortify its innovative leadership in the development industry. In 2023 the large panel business will increase sales of QD-OLED by expanding the lineup and further enhancing performance, while also working towards profitability.
Like many of Samsung’s US competitors in the technology space, and unlike most companies in the display industry, Samsung’s balance sheet boasts a mountain of cash. Samsung had KRW 128.8T ($96.1B) of cash and short-term investments at the end of Q3 and shows minimal debt and negative net debt/equity. With solid profits in Q3 Samsung generated KRW 6.7T ($5.0B) in free cash flow.
Samsung’s inventory was already high at the end of Q2 but increased further in Q3. Samsung inventory increased by KRW 5T Q/Q. A part of the increase was DX inventory to ensure stable supply. Most of the increase was memory and Samsung will continue to work to manage inventory to balanced levels.
Although Samsung’s semiconductor business remains its main profit driver, Samsung also outperforms its competitors (except for Apple) in its smartphone and TV device businesses and in its display business. In display, Samsung’s strategic decision to exit LCD and build an OLED smartphone panel business has paid off with handsome profits.
本記事の出典調査レポート
Quarterly Display Supply Chain Financial Health Report
一部実データ付きサンプルをご返送
ご案内手順
1) まずは「お問い合わせフォーム」経由のご連絡にて、ご紹介資料、国内販売価格、一部実データ付きサンプルをご返信します。2) その後、DSCCアジア代表・田村喜男アナリストによる「本レポートの強み~DSCC独自の分析手法とは」のご説明 (お電話またはWEB面談) の上、お客様のミッションやお悩みをお聞かせください。本レポートを主候補に、課題解決に向けた最適サービスをご提案させていただきます。 3) ご購入後も、掲載内容に関するご質問を国内お客様サポート窓口が承り、質疑応答ミーティングを通じた国内外アナリスト/コンサルタントとの積極的な交流をお手伝いします。